Complement = variable with a bar over it
Literal = variable or its complement
Implicant = product of literal == (AB) , (ABC) ...
Minterm = product (AND) taht includes all input variables == (ABC) , (A`BC) ...
Sum of Products Form (SOP)

First make truth table to Canonical From , than optimize it using axioms or other boolean expression tool.
Product of Sums (POS) = Demorgan of SOP

Building larger block like decoder, mutiplexer to abstract and hide logic gate.
Decoder
n inputs and 2^n outputs

those As could be the address of row in DRAM or instruction in the program (opcode) and we use decoder to get what that bit pattern tells us.
Multiplexer , Selector
Selects one of the N inputs to connect it to the input

we have 2 input , 1 select , 1 output
Full Adder
Binary addition

handling just single bit we can use this as module and implement n bits adder.

power of abstraction.
Programmable Logic Array (PLA)
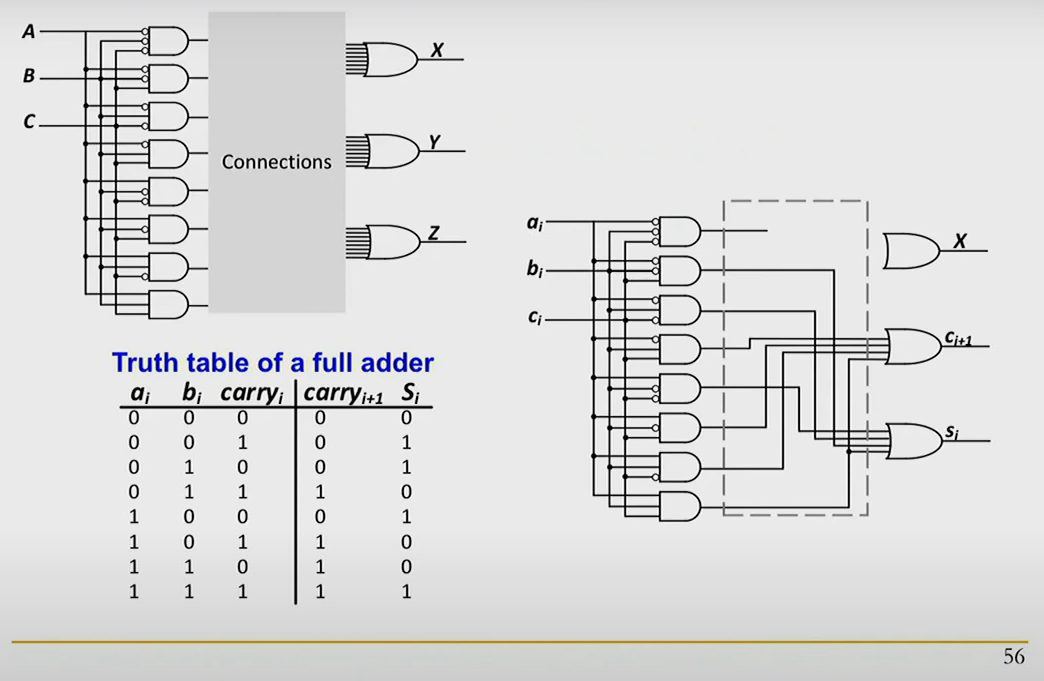
we can see that first and gate and or gate is not used
{AND , OR , NOT} is logically complete. also {NAND} , {NOR} gate is complete by itself.
Tri State Buffer

E stands for Enable. Z means floating value , it doesn't mean it is wrong value it means output is not driven by certain input in this case A.

needed when we control CPU and memory.
'Computer Architecture > C.A (ETH Zürich, Spring 2020)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Lecture 8: Timing & Verification (0) | 2021.06.11 |
|---|---|
| Lecture 7b: HW Description Lang. & Verilog (0) | 2021.06.08 |
| Lecture 6: Sequential Logic Design (0) | 2021.06.08 |
| Lecture 4: Combinational Logic 1 (0) | 2021.06.03 |
| Lecture 2b: Mysteries in Comp. Arch. (0) | 2021.06.02 |