in this lecture we simplify the setting
the enviromnet is assumed to have only a single state , actions no longer have long-term consequences in the enviroment
actions still do impact immediate reward , not environment , other observation can be ignored because env has only 1 state
exploitation = maximise performance based on current knowledge
exploration = increase knowledge , exposing self to new data
The Multi-Armed Bandit

values and regret

regret is not a random thing it is more like opportunity cost
more regret you get the worse your doing
regret

total regret is random quantity because it depends on the action we take , and action can be random because policy can be random
algorithms
action values

if we selection certain action "a" at time step n indicator function will be 1 otherwise 0

In addition to calculating the average , we can just incrementally update estimtate action value
Greedy
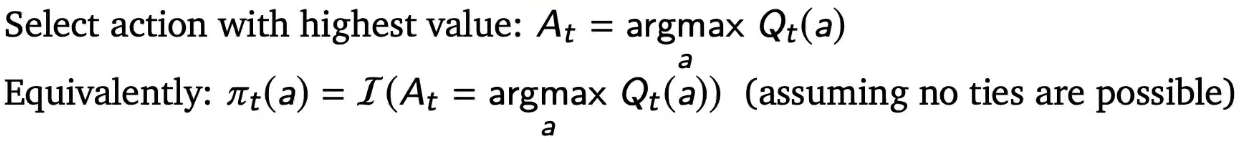
pie indicates policy at time t given action "a" == just picking "a" that gives highest estimate action value

with greedy policy in this case agent will never select action "a"
epslion greedy algorithm
as seen in example above greedy can stuck on an suboptimal action forever

However, the algorithm will continue to search even if it finds an optimal policy.
policy search = want to learn policies directly ,instead of learning values
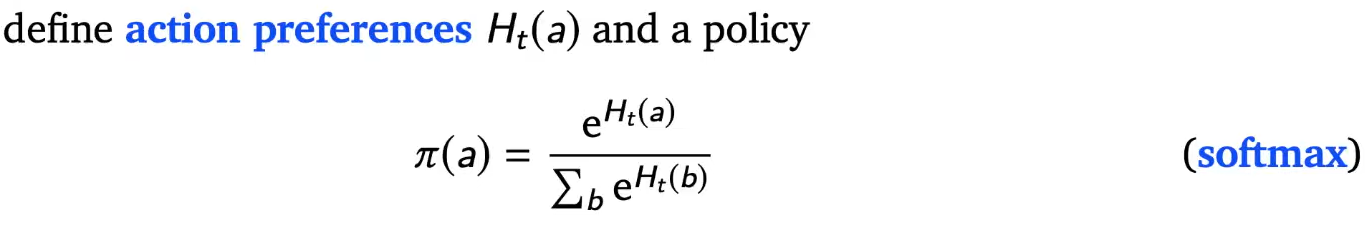
define action preferences and normalize it with softmax
goal is to learn by optimising the preferences
policy gradients (gradient bandits) = want to update policy parameters such that expected value increases , theta is policy parameter

instead of actually computing expectation , we can sample some and use stochastic gradient


preference of selelcting action At will only increate be cause all the seoncd term values are positve (if reward is positive)
at the same time preference of selecting other action will goes down little bit (below equation) , the amount of decrease depends on how likely they are to be selected
preferenecs for actions with higher rewards increase more (or decrease less), making them more likely to be selected again , but can be stuck into local optimal

since it sums up to zero we can just subtract baseline
'AI > RL (2021 DeepMind x UCL )' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Lecture 5: Model-free Prediction (part 1) (0) | 2021.12.04 |
|---|---|
| Lecture 4: Theoretical Fund. of Dynamic Programming Algorithms (0) | 2021.11.27 |
| Lecture 3: MDPs and Dynamic Programming (0) | 2021.11.20 |
| Lecture 2: Exploration and Exploitation (part 2) (0) | 2021.11.14 |
| Lecture 1: Introduction to Reinforcement Learning (0) | 2021.11.07 |