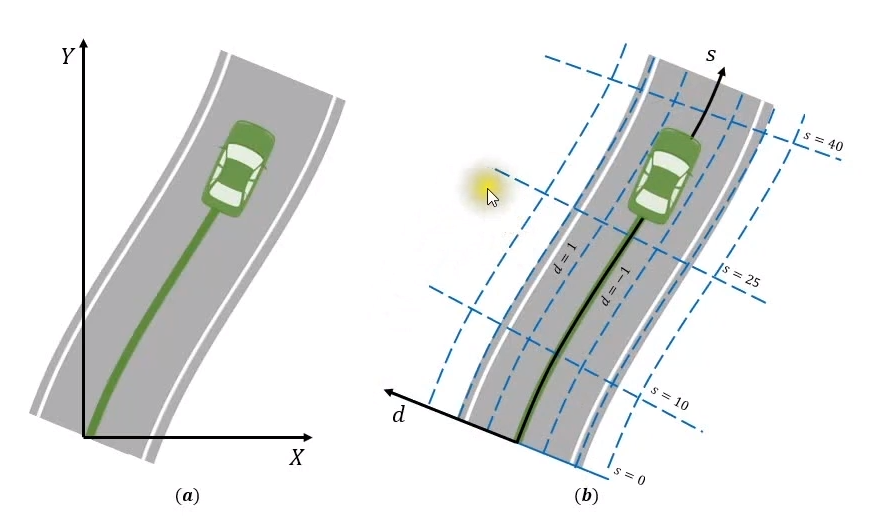
Frenet Frame
Figure (A) 은 Cartesian frame을 Figure (B)는 Frenet frame 을 표현
도로 형상의 방향으로 s-axis 가 도로와 수직방향으로 d-axis가 펼쳐져서 작관적이고 편리하다.

종방향, 횡방향, 속도를 각가 다른 polynomial 을 적용해서 풀어야 한다. 각각 다른 경로를 생성한다.

각기 다른 경로들을 합쳐야한다. Long 의 갯수와 lateral 의 갯수의 곱 만큼 경로를 뽑아내고 그중에 가장 조건에 알맞은 trajectory를 선택한다.
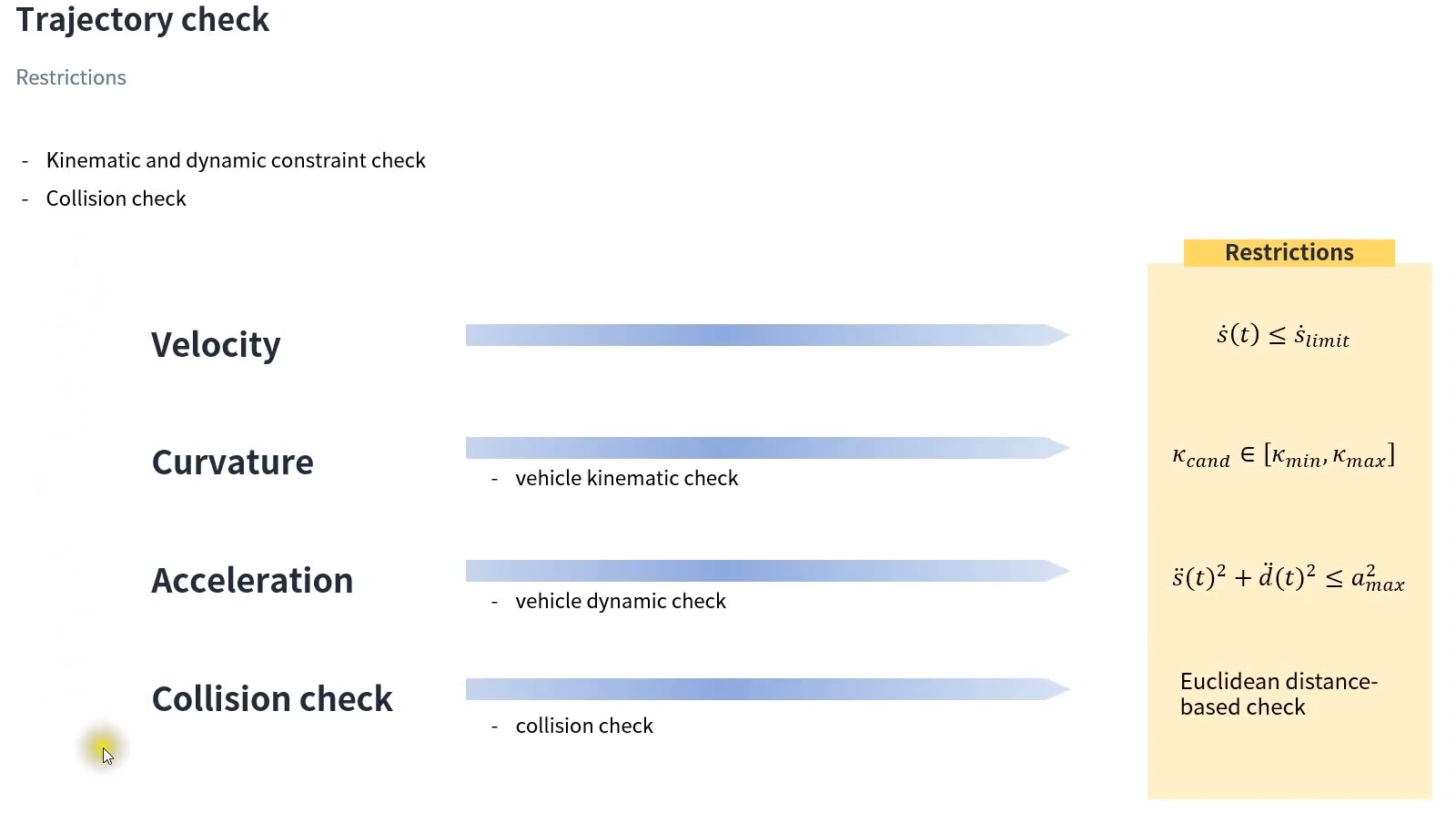
위에 언급한 조건들이다. 이것들을 만족하는 것들중 최적화된 path를 골라 내야한다.
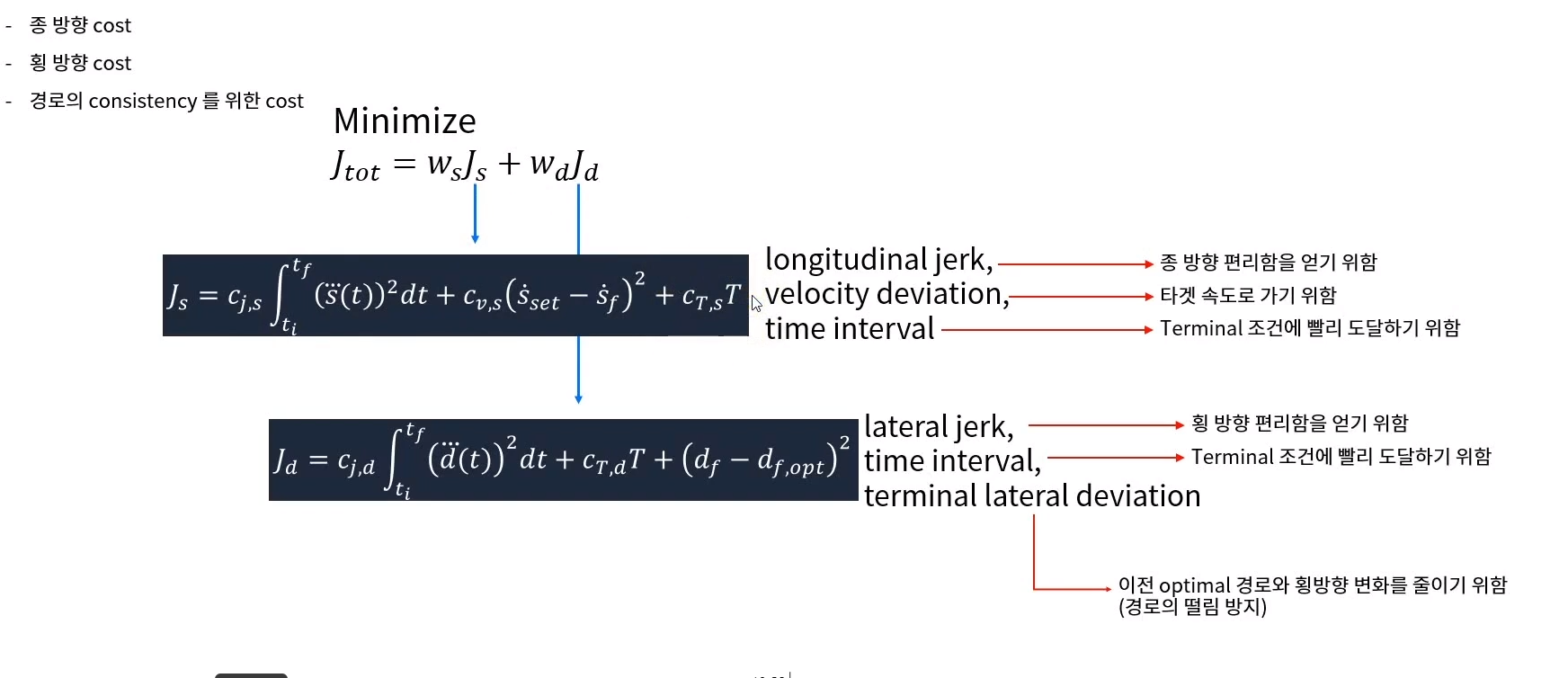
횡방향 cost , 종방향 cost , 경로의 cosistency cost를 최소로 하는 최적화 문제를 풀어줘야 한다. 사람은 횡방향 에 더민감하게 반응함으로 편의르르 위해 횡방향 cost에 weight를 더 많이 부가하는 편이다.
Python implemenation
#-*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
import pickle
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from copy import deepcopy
import sys
import math
from numpy import *
from matplotlib import *
with open('./map/map_coord_proto2.pkl', 'rb') as f:
map_coord = pickle.load(f)
map_in = map_coord['Lane_inner']
map_center = map_coord['Lane_center']
map_out = map_coord['Lane_outer']
wp_in = map_coord['waypoint_inner']
wp_out = map_coord['waypoint_outer']
# initialize
V_MAX = 2 # maximum velocity [m/s]
ACC_MAX = 2 # maximum acceleration [m/ss]
K_MAX = 4 # maximum curvature [1/m]
TARGET_SPEED = 1 # target speed [m/s]
LANE_WIDTH = 0.39 # lane width [m]
COL_CHECK = 0.25 # collision check distance [m]
MIN_T = 1 # minimum terminal time [s]
MAX_T = 2 # maximum terminal time [s]
DT_T = 0.5 # dt for terminal time [s] : MIN_T 에서 MAX_T 로 어떤 dt 로 늘려갈지를 나타냄
DT = 0.1 # timestep for update
# cost weights
K_J = 0.1 # weight for jerk
K_T = 0.1 # weight for terminal time
K_D = 1.0 # weight for consistency
K_V = 1.0 # weight for getting to target speed
K_LAT = 1.0 # weight for lateral direction
K_LON = 1.0 # weight for longitudinal direction
SIM_STEP = 100 # simulation step
SHOW_ANIMATION = True # plot 으로 결과 보여줄지 말지
# Vehicle parameters - plot 을 위한 파라미터
LENGTH = 0.39 # [m]
WIDTH = 0.19 # [m]
BACKTOWHEEL = 0.1 # [m]
WHEEL_LEN = 0.03 # [m]
WHEEL_WIDTH = 0.02 # [m]
TREAD = 0.07 # [m]
WB = 0.22 # [m]
# lateral planning 시 terminal position condition 후보 (양 차선 중앙)
DF_SET = np.array([LANE_WIDTH/2, -LANE_WIDTH/2])
def next_waypoint(x, y, mapx, mapy):
closest_wp = get_closest_waypoints(x, y, mapx, mapy)
map_vec = [mapx[closest_wp + 1] - mapx[closest_wp], mapy[closest_wp + 1] - mapy[closest_wp]]
ego_vec = [x - mapx[closest_wp], y - mapy[closest_wp]]
direction = np.sign(np.dot(map_vec, ego_vec))
if direction >= 0:
next_wp = closest_wp + 1
else:
next_wp = closest_wp
return next_wp
def get_closest_waypoints(x, y, mapx, mapy):
min_len = 1e10
closeset_wp = 0
for i in range(len(mapx)):
_mapx = mapx[i]
_mapy = mapy[i]
dist = get_dist(x, y, _mapx, _mapy)
if dist < min_len:
min_len = dist
closest_wp = i
return closest_wp
def get_dist(x, y, _x, _y):
return np.sqrt((x - _x)**2 + (y - _y)**2)
def get_frenet(x, y, mapx, mapy):
next_wp = next_waypoint(x, y, mapx, mapy)
prev_wp = next_wp -1
n_x = mapx[next_wp] - mapx[prev_wp]
n_y = mapy[next_wp] - mapy[prev_wp]
x_x = x - mapx[prev_wp]
x_y = y - mapy[prev_wp]
proj_norm = (x_x*n_x+x_y*n_y)/(n_x*n_x+n_y*n_y)
proj_x = proj_norm*n_x
proj_y = proj_norm*n_y
#-------- get frenet d
frenet_d = get_dist(x_x,x_y,proj_x,proj_y)
ego_vec = [x-mapx[prev_wp], y-mapy[prev_wp], 0];
map_vec = [n_x, n_y, 0];
d_cross = np.cross(ego_vec,map_vec)
if d_cross[-1] > 0:
frenet_d = -frenet_d;
#-------- get frenet s
frenet_s = 0;
for i in range(prev_wp):
frenet_s = frenet_s + get_dist(mapx[i],mapy[i],mapx[i+1],mapy[i+1]);
frenet_s = frenet_s + get_dist(0,0,proj_x,proj_y);
return frenet_s, frenet_d
def get_cartesian(s, d, mapx, mapy, maps):
prev_wp = 0
s = np.mod(s, maps[-2])
while(s > maps[prev_wp+1]) and (prev_wp < len(maps)-2):
prev_wp = prev_wp + 1
next_wp = np.mod(prev_wp+1,len(mapx))
dx = (mapx[next_wp]-mapx[prev_wp])
dy = (mapy[next_wp]-mapy[prev_wp])
heading = np.arctan2(dy, dx) # [rad]
# the x,y,s along the segment
seg_s = s - maps[prev_wp];
seg_x = mapx[prev_wp] + seg_s*np.cos(heading);
seg_y = mapy[prev_wp] + seg_s*np.sin(heading);
perp_heading = heading + 90 * np.pi/180;
x = seg_x + d*np.cos(perp_heading);
y = seg_y + d*np.sin(perp_heading);
return x, y, heading
class QuinticPolynomial:
def __init__(self, xi, vi, ai, xf, vf, af, T):
# calculate coefficient of quintic polynomial
# used for lateral trajectory
self.a0 = xi
self.a1 = vi
self.a2 = 0.5*ai
A = np.array([[T**3, T**4, T**5],
[3*T**2, 4*T**3, 5*T** 4],
[6*T, 12*T**2, 20*T**3]])
b = np.array([xf - self.a0 - self.a1*T - self.a2*T**2,
vf - self.a1 - 2*self.a2*T,
af - 2*self.a2])
x = np.linalg.solve(A, b)
self.a3 = x[0]
self.a4 = x[1]
self.a5 = x[2]
# calculate postition info.
def calc_pos(self, t):
x = self.a0 + self.a1*t + self.a2*t**2 + self.a3*t**3 + self.a4*t**4 + self.a5 * t ** 5
return x
# calculate velocity info.
def calc_vel(self, t):
v = self.a1 + 2*self.a2*t + 3*self.a3*t**2 + 4*self.a4*t**3 + 5*self.a5*t**4
return v
# calculate acceleration info.
def calc_acc(self, t):
a = 2*self.a2 + 6*self.a3*t + 12*self.a4*t**2 + 20*self.a5*t**3
return a
# calculate jerk info.
def calc_jerk(self, t):
j = 6*self.a3 + 24*self.a4*t + 60*self.a5*t**2
return j
class QuarticPolynomial:
def __init__(self, xi, vi, ai, vf, af, T):
# calculate coefficient of quartic polynomial
# used for longitudinal trajectory
self.a0 = xi
self.a1 = vi
self.a2 = 0.5*ai
A = np.array([[3*T**2, 4*T**3],
[6*T, 12*T**2]])
b = np.array([vf - self.a1 - 2*self.a2*T,
af - 2*self.a2])
x = np.linalg.solve(A, b)
self.a3 = x[0]
self.a4 = x[1]
# calculate postition info.
def calc_pos(self, t):
x = self.a0 + self.a1*t + self.a2*t**2 + self.a3*t**3 + self.a4*t**4
return x
# calculate velocity info.
def calc_vel(self, t):
v = self.a1 + 2*self.a2*t + 3*self.a3*t**2 + 4*self.a4*t**3
return v
# calculate acceleration info.
def calc_acc(self, t):
a = 2*self.a2 + 6*self.a3*t + 12*self.a4*t**2
return a
# calculate jerk info.
def calc_jerk(self, t):
j = 6*self.a3 + 24*self.a4*t
return j
class FrenetPath:
def __init__(self):
# time
self.t = []
# lateral traj in Frenet frame
self.d = []
self.d_d = []
self.d_dd = []
self.d_ddd = []
# longitudinal traj in Frenet frame
self.s = []
self.s_d = []
self.s_dd = []
self.s_ddd = []
# cost
self.c_lat = 0.0
self.c_lon = 0.0
self.c_tot = 0.0
# combined traj in global frame
self.x = []
self.y = []
self.yaw = []
self.ds = []
self.kappa = []
def calc_frenet_paths(si, si_d, si_dd, sf_d, sf_dd, di, di_d, di_dd, df_d, df_dd, opt_d):
frenet_paths = []
# generate path to each offset goal
for df in DF_SET:
# Lateral motion planning
for T in np.arange(MIN_T, MAX_T+DT_T, DT_T):
fp = FrenetPath()
lat_traj = QuinticPolynomial(di, di_d, di_dd, df, df_d, df_dd, T)
fp.t = [t for t in np.arange(0.0, T, DT)]
fp.d = [lat_traj.calc_pos(t) for t in fp.t]
fp.d_d = [lat_traj.calc_vel(t) for t in fp.t]
fp.d_dd = [lat_traj.calc_acc(t) for t in fp.t]
fp.d_ddd = [lat_traj.calc_jerk(t) for t in fp.t]
# Longitudinal motion planning (velocity keeping)
tfp = deepcopy(fp)
lon_traj = QuarticPolynomial(si, si_d, si_dd, sf_d, sf_dd, T)
tfp.s = [lon_traj.calc_pos(t) for t in fp.t]
tfp.s_d = [lon_traj.calc_vel(t) for t in fp.t]
tfp.s_dd = [lon_traj.calc_acc(t) for t in fp.t]
tfp.s_ddd = [lon_traj.calc_jerk(t) for t in fp.t]
# 경로 늘려주기 (In case T < MAX_T)
for _t in np.arange(T, MAX_T, DT):
tfp.t.append(_t)
tfp.d.append(tfp.d[-1])
_s = tfp.s[-1] + tfp.s_d[-1] * DT
tfp.s.append(_s)
tfp.s_d.append(tfp.s_d[-1])
tfp.s_dd.append(tfp.s_dd[-1])
tfp.s_ddd.append(tfp.s_ddd[-1])
tfp.d_d.append(tfp.d_d[-1])
tfp.d_dd.append(tfp.d_dd[-1])
tfp.d_ddd.append(tfp.d_ddd[-1])
J_lat = sum(np.power(tfp.d_ddd, 2)) # lateral jerk
J_lon = sum(np.power(tfp.s_ddd, 2)) # longitudinal jerk
# cost for consistency
d_diff = (tfp.d[-1] - opt_d) ** 2
# cost for target speed
v_diff = (TARGET_SPEED - tfp.s_d[-1]) ** 2
# lateral cost
tfp.c_lat = K_J * J_lat + K_T * T + K_D * d_diff
# logitudinal cost
tfp.c_lon = K_J * J_lon + K_T * T + K_V * v_diff
# total cost combined
tfp.c_tot = K_LAT * tfp.c_lat + K_LON * tfp.c_lon
frenet_paths.append(tfp)
return frenet_paths
def calc_global_paths(fplist, mapx, mapy, maps):
# transform trajectory from Frenet to Global
for fp in fplist:
for i in range(len(fp.s)):
_s = fp.s[i]
_d = fp.d[i]
_x, _y, _ = get_cartesian(_s, _d, mapx, mapy, maps)
fp.x.append(_x)
fp.y.append(_y)
for i in range(len(fp.x) - 1):
dx = fp.x[i + 1] - fp.x[i]
dy = fp.y[i + 1] - fp.y[i]
fp.yaw.append(np.arctan2(dy, dx))
fp.ds.append(np.hypot(dx, dy))
fp.yaw.append(fp.yaw[-1])
fp.ds.append(fp.ds[-1])
# calc curvature
for i in range(len(fp.yaw) - 1):
yaw_diff = fp.yaw[i + 1] - fp.yaw[i]
yaw_diff = np.arctan2(np.sin(yaw_diff), np.cos(yaw_diff))
fp.kappa.append(yaw_diff / fp.ds[i])
return fplist
def collision_check(fp, obs, mapx, mapy, maps):
for i in range(len(obs[:, 0])):
# get obstacle's position (x,y)
obs_xy = get_cartesian( obs[i, 0], obs[i, 1], mapx, mapy, maps)
d = [((_x - obs_xy[0]) ** 2 + (_y - obs_xy[1]) ** 2)
for (_x, _y) in zip(fp.x, fp.y)]
collision = any([di <= COL_CHECK ** 2 for di in d])
if collision:
return True
return False
def check_path(fplist, obs, mapx, mapy, maps):
ok_ind = []
for i, _path in enumerate(fplist):
acc_squared = [(abs(a_s**2 + a_d**2)) for (a_s, a_d) in zip(_path.s_dd, _path.d_dd)]
if any([v > V_MAX for v in _path.s_d]): # Max speed check
continue
elif any([acc > ACC_MAX**2 for acc in acc_squared]):
continue
elif any([abs(kappa) > K_MAX for kappa in fplist[i].kappa]): # Max curvature check
continue
elif collision_check(_path, obs, mapx, mapy, maps):
continue
ok_ind.append(i)
return [fplist[i] for i in ok_ind]
def frenet_optimal_planning(si, si_d, si_dd, sf_d, sf_dd, di, di_d, di_dd, df_d, df_dd, obs, mapx, mapy, maps, opt_d):
fplist = calc_frenet_paths(si, si_d, si_dd, sf_d, sf_dd, di, di_d, di_dd, df_d, df_dd, opt_d)
fplist = calc_global_paths(fplist, mapx, mapy, maps)
fplist = check_path(fplist, obs, mapx, mapy, maps)
# find minimum cost path
min_cost = float("inf")
opt_traj = None
opt_ind = 0
for fp in fplist:
if min_cost >= fp.c_tot:
min_cost = fp.c_tot
opt_traj = fp
_opt_ind = opt_ind
opt_ind += 1
try:
_opt_ind
except NameError:
print(" No solution ! ")
return fplist, _opt_ind
def plot_car(x, y, yaw, steer=0.0, cabcolor="-r", truckcolor="-k"): # pragma: no cover
outline = np.array([[-BACKTOWHEEL, (LENGTH - BACKTOWHEEL), (LENGTH - BACKTOWHEEL), -BACKTOWHEEL, -BACKTOWHEEL],
[WIDTH / 2, WIDTH / 2, - WIDTH / 2, -WIDTH / 2, WIDTH / 2]])
fr_wheel = np.array([[WHEEL_LEN, -WHEEL_LEN, -WHEEL_LEN, WHEEL_LEN, WHEEL_LEN],
[-WHEEL_WIDTH - TREAD, -WHEEL_WIDTH - TREAD, WHEEL_WIDTH - TREAD, WHEEL_WIDTH - TREAD, -WHEEL_WIDTH - TREAD]])
rr_wheel = np.copy(fr_wheel)
fl_wheel = np.copy(fr_wheel)
fl_wheel[1, :] *= -1
rl_wheel = np.copy(rr_wheel)
rl_wheel[1, :] *= -1
Rot1 = np.array([[math.cos(yaw), math.sin(yaw)],
[-math.sin(yaw), math.cos(yaw)]])
Rot2 = np.array([[math.cos(steer), math.sin(steer)],
[-math.sin(steer), math.cos(steer)]])
fr_wheel = (fr_wheel.T.dot(Rot2)).T
fl_wheel = (fl_wheel.T.dot(Rot2)).T
fr_wheel[0, :] += WB
fl_wheel[0, :] += WB
fr_wheel = (fr_wheel.T.dot(Rot1)).T
fl_wheel = (fl_wheel.T.dot(Rot1)).T
outline = (outline.T.dot(Rot1)).T
rr_wheel = (rr_wheel.T.dot(Rot1)).T
rl_wheel = (rl_wheel.T.dot(Rot1)).T
outline[0, :] += x
outline[1, :] += y
fr_wheel[0, :] += x
fr_wheel[1, :] += y
rr_wheel[0, :] += x
rr_wheel[1, :] += y
fl_wheel[0, :] += x
fl_wheel[1, :] += y
rl_wheel[0, :] += x
rl_wheel[1, :] += y
plt.plot(np.array(outline[0, :]).flatten(),
np.array(outline[1, :]).flatten(), truckcolor)
plt.plot(np.array(fr_wheel[0, :]).flatten(),
np.array(fr_wheel[1, :]).flatten(), truckcolor)
plt.plot(np.array(rr_wheel[0, :]).flatten(),
np.array(rr_wheel[1, :]).flatten(), truckcolor)
plt.plot(np.array(fl_wheel[0, :]).flatten(),
np.array(fl_wheel[1, :]).flatten(), truckcolor)
plt.plot(np.array(rl_wheel[0, :]).flatten(),
np.array(rl_wheel[1, :]).flatten(), truckcolor)
plt.plot(x, y, "*")
def test():
# map waypoints
mapx = map_center[:,0]
mapy = map_center[:,1]
# static obstacles
obs = np.array([[3.0, WIDTH],
[5, -WIDTH],
[7, WIDTH],
[8.5, -WIDTH]
])
# get maps
maps = np.zeros(mapx.shape)
for i in range(len(mapx)):
x = mapx[i]
y = mapy[i]
sd = get_frenet(x, y, mapx, mapy)
maps[i] = sd[0]
# get global position info. of static obstacles
obs_global = np.zeros(obs.shape)
for i in range(len(obs[:,0])):
_s = obs[i,0]
_d = obs[i,1]
xy = get_cartesian(_s, _d, mapx, mapy, maps)
obs_global[i] = xy[:-1]
# 자챠량 관련 initial condition
x = -LANE_WIDTH
y = 0
yaw = 90 * np.pi/180
v = 0.5
a = 0
s, d = get_frenet(x, y, mapx, mapy);
x, y, yaw_road = get_cartesian(s, d, mapx, mapy, maps)
yawi = yaw - yaw_road
# s 방향 초기조건
si = s
si_d = v*np.cos(yawi)
si_dd = a*np.cos(yawi)
sf_d = TARGET_SPEED
sf_dd = 0
# d 방향 초기조건
di = d
di_d = v*np.sin(yawi)
di_dd = a*np.sin(yawi)
df_d = 0
df_dd = 0
opt_d = di
# 시뮬레이션 수행 (SIM_STEP 만큼)
plt.figure(figsize=(7,10))
for step in range(SIM_STEP):
# optimal planning 수행 (output : valid path & optimal path index)
path, opt_ind = frenet_optimal_planning(si, si_d, si_dd,
sf_d, sf_dd, di, di_d, di_dd, df_d, df_dd, obs, mapx, mapy, maps, opt_d)
'''
다음 시뮬레이션 step 에서 사용할 initial condition update.
본 파트에서는 planning 만 수행하고 control 은 따로 수행하지 않으므로,
optimal trajectory 중 현재 위치에서 한개 뒤 index 를 다음 step 의 초기초건으로 사용.
'''
si = path[0].s[1]
si_d = path[0].s_d[1]
si_dd = path[0].s_dd[1]
di = path[0].d[1]
di_d = path[0].d_d[1]
di_dd = path[0].d_dd[1]
# consistency cost를 위해 update
opt_d = path[opt_ind].d[-1]
if SHOW_ANIMATION: # pragma: no cover
plt.cla()
# for stopping simulation with the esc key.
plt.gcf().canvas.mpl_connect(
'key_release_event',
lambda event: [exit(0) if event.key == 'escape' else None])
plt.plot(map_center[:,0], map_center[:,1], 'k', linewidth=2)
plt.plot(map_in[:,0], map_in[:,1], 'k', linewidth=2)
plt.plot(map_out[:,0], map_out[:,1], 'k', linewidth=2)
plt.plot(wp_in[:,0], wp_in[:,1], color='slategray', linewidth=2, alpha=0.5)
plt.plot(wp_out[:,0], wp_out[:,1], color='slategray', linewidth=2, alpha=0.5)
# plot obstacle
for ob in obs_global:
plt.plot(ob[0], ob[1], "s", color="crimson", MarkerSize=15, alpha=0.6)
for i in range(len(path)):
plt.plot(path[i].x, path[i].y, "-", color="crimson", linewidth=1.5, alpha=0.6)
plt.plot(path[opt_ind].x, path[opt_ind].y, "o-", color="dodgerblue", linewidth=3)
# plot car
plot_car(path[opt_ind].x[0], path[opt_ind].y[0], path[opt_ind].yaw[0], steer=0)
plt.axis('equal')
plt.title("[Simulation] v : " + str(si_d)[0:4] + " m/s")
plt.grid(True)
plt.xlabel("X [m]")
plt.ylabel("Y [m]")
plt.pause(0.01)
# input("Press enter to continue...")
if __name__ == "__main__":
test()
QuarticPolynomal class == 종방향 경로 생성, 안에 position , velocity , acceleration ,jerk 를 계산해서 return 해주는 함수를 가지고 있다. 생성자의 인자로는 initial condition (위치,속도, 가속도) , terminal condition (위치,속도,가속도) ,terminal time : terminal condition 을 만족시키는 시간 들이 주어진다.
calc_frenet_paths == 횡방향 경로 생성은 QuinticPolynomial (5차) , 종방향 경로 생성은 QuarticPolynomial (4차) 로 구해준다. cost를 계산하는 역할과 경로를 늘려주는 후 처리 역할 도 한다.
calc_global_paths == Frenet frame에서 짠 코드를 다시 Cartesian frame으로 변경을 해준다.
check_path == 속도,가속도 ,곡률을 check 하고 장애물과의 충돌도 확인 하는 collision_check 가 존재한다. 위의 코드는 그냥 Euclidean distance 기반으로 충돌 판단을 합니다.
frenet_optimal_planning == trajectory 후보 중 cost가 가장 낮은 optimal 한 경로를 선택한다.
장애물들은 static 하게 main 함수에서 static하게 생성해준다. 여러 parameter 들을 initialize 해준다.
'자율주행 > 차량제어' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 외국 기업 사례 (모듈화 보다는 딥러닝 기반) (0) | 2021.02.04 |
|---|---|
| A generic driving strategy for urban environment (0) | 2021.02.03 |
| Path Planning Algorithms (0) | 2021.02.03 |
| MPC(model predictive control) (2) | 2021.02.02 |
| PID ,Kalman (0) | 2021.02.02 |