pipe system call
Creating pipe is similar to opening 2 files. A successful call to pipe() returns 2 open file descriptors in the array fd. one contains the read descriptor of the pipe, fd[0] , and the other contains the write descriptor fo the pipe fd[1].
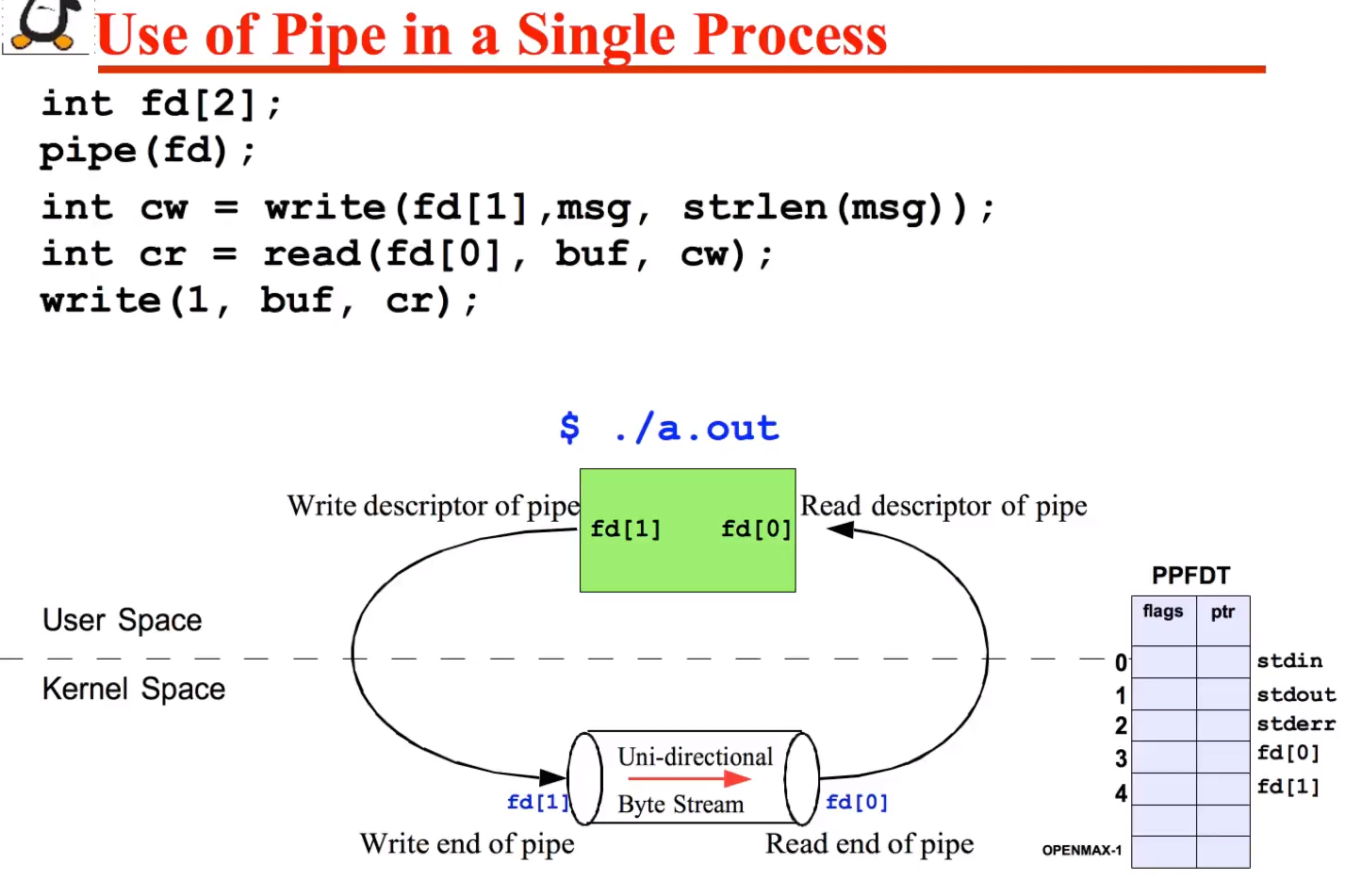
if pipe(fd) fails it returns -1.

to make parent process writer and child process reader we close fd[0] from parent process and close fd[1] form child process.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define SIZE 1024
int main(){
int fd[2];
int rv = pipe(fd);
//create a child process
pid_t cpid = fork();
//parent code (parent is writer process)
if (cpid != 0) {
close(fd[0]);
const char * msg = "Welcome to Communication using pipes\n";
write(fd[1], msg,strlen(msg));
waitpid(cpid, NULL, 0);
exit(0);
}
//child code (child is reader process)
else {
close(fd[1]);
char buff[SIZE];
memset(buff, '\0',SIZE);
fprintf(stderr,"Message sent from parent is: ");
int n = read(fd[0],buff,SIZE);
write(1,buff,n);
exit(0);
}
}notice we close parent's fd[0] and child's fd[1].
Named pipe

the actual input doesn't goto fifo1 , instead it goes to kernel's pipe and will be blocked until other user consume the pipe.
writer .c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(){
char buff[1024];
mknod("myfifo", S_IFIFO | 0666, 0);
printf("Waiting for readers....\n");
int writefd = open("myfifo", O_WRONLY);
printf("Got a reader -- type some text to be sent\n");
//read from stdin and write to the fifo
while(fgets(buff, 1023, stdin))
write(writefd, buff, strlen(buff));
return 0;
}
reader.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(){
char buff[1024];
int num;
mknod("myfifo", S_IFIFO | 0666, 0);
printf("Waiting for writers....\n");
int readfd = open("myfifo", O_RDONLY);
printf("Got a writer\n");
do{//keep reading from myfifo
num = read(readfd, buff, 1024);
buff[num] = '\0';
//display the contents on stdout
printf("Reader read %d bytes: %s\n",num, buff);
}while(num > 0); // read until EOF
return 0;
}write(with fgets) to named pipe("myfifo") and read from it and display the content to stdout(terminal).

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/errno.h>
#define MESSAGE1 "\n\n\nThis is a message from student:\n\t This program is 2 difficult to understand sir!\n"
int main(){
char buff[1024];
int readfd, writefd, n, size;
//open fifo1 for writing
writefd = open ("/tmp/fifo1", 1);
//open fifo2 for reading
readfd = open ("/tmp/fifo2", 0);
//Write a message in fifo1 to be sent to other process
write(writefd, MESSAGE1, strlen(MESSAGE1) + 1);
//Read a message from fifo2
n = read(readfd, buff, 1024);
//Writes the msg sent by other program on screen
write(1, buff, n);
close (readfd);
close (writefd);
//remove fifos now that we are done using them
if(unlink("/tmp/fifo1") <0){
perror("Client unlink FIFO1");
exit (1);
}
if(unlink("/tmp/fifo2") <0){
perror("Client unlink FIFO2");
exit (1);
}
return 0;
}#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/errno.h>
#define MESSAGE2 "\nResponse from Teacher: \n\tThere is no short cut to hard work! So WORK HARD....\n\n\n\n"
int main(){
char buff[1024];
int rv, readfd, writefd, n, size;
//create fifo1 using mknod system call
mknod("/tmp/fifo1", S_IFIFO | 0666, 0);
//create fifo2 using mkfifo library call
rv = mkfifo("/tmp/fifo2", 0666);
if(rv == -1){
unlink("/tmp/fifo1");
perror("mkfifo failed");
exit(1);
}
//Open fifo1 for reading purpose
readfd = open ("/tmp/fifo1", 0);
//Open fifo2 for writing purpose
writefd = open ("/tmp/fifo2", 1);
//Make a blocking call on fifo1
n=read(readfd, buff, 1024);
//Display that message on screen
write(1, buff, n);
//Send a response to other program via fifo2
sleep(20);
write(writefd, MESSAGE2, strlen(MESSAGE2) + 1);
close (readfd);
close (writefd);
return 0;
}student open fifo1 in write mode , open fifo2 in read mode.
write message on fifo1 so teacher can read.
and read from fifo2 to see teacher's message.
and than delete all fifo.
teacher create 2 fifo.
open fifo1 in read mode , open fifo2 in write mode.
read from fifo1 (blocking) and write that into fd1 (stdout,terminal).
'Operating System > System Programming(Arif Butt)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Lec29, 30) Programming With Shared Memory , Memory Mapped Files (0) | 2021.07.24 |
|---|---|
| Lec28) Message Queues (0) | 2021.07.21 |
| Lec25) Design and Code Of Signal Handlers (0) | 2021.07.17 |
| Lec24) Overview Of UNIX IPC And Signals On The Shell (0) | 2021.07.16 |
| Lec23 Multi Threaded Programming (0) | 2021.07.15 |