
we can iterate directory by looping through readdir() with given pointer stream.
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
extern int errno;
int main(){
printf("Directory scan of /home/: \n");
DIR* dp = opendir("/home");
chdir("/home");
errno = 0;
struct dirent* entry;
while(1){
entry = readdir(dp);
if(entry == NULL && errno != 0){
perror("readdir");
return errno;
}
if(entry == NULL && errno == 0){
printf("\nEnd of directory\n");
return 0;
}
printf("%s ",entry->d_name);
}
closedir(dp);
return 0;
}we are getting needed pointer from opendir() function and pass result to readdir.
if statement is for error handling.
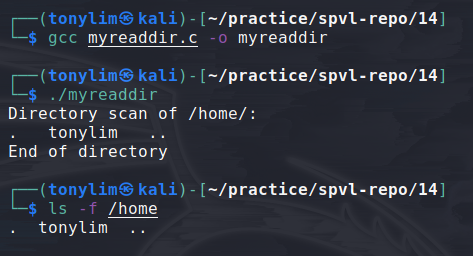
display contents of home directory. -f option does the same thing as above code.
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <string.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
extern int errno;
void do_ls(char*);
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
if (argc == 1){
printf("Directory listing of pwd:\n");
do_ls(".");
}
else{
int i = 0;
while(++i < argc){
printf("Directory listing of %s:\n", argv[i] );
do_ls(argv[i]);
}
}
return 0;
}
void do_ls(char * dir)
{
struct dirent * entry;
DIR * dp = opendir(dir);
if (dp == NULL){
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot open directory:%s\n",dir);
return;
}
errno = 0;
while((entry = readdir(dp)) != NULL){
if(entry == NULL && errno != 0){
perror("readdir failed");
exit(1);
}else{
if(entry->d_name[0] == '.')
continue;
} printf("%s\n",entry->d_name);
}
closedir(dp);
}if there are only one argument (directory) than we just print current directory using do_ls function.
if there are more than one we just loop through.
stat() system call

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <time.h>
void show_stat_info(char*);
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
if(argc != 2){
fprintf(stderr, "Incorrect number of arguments\n");
exit(1);
}
show_stat_info(argv[1]);
return 0;
}
void show_stat_info(char *fname){
struct stat info;
int rv = lstat(fname, &info);
if (rv == -1){
perror("stat failed");
exit(1);
}
printf("mode: %o\n", info.st_mode);
printf("link count: %ld\n", info.st_nlink);
printf("user: %d\n", info.st_uid);
printf("group: %d\n", info.st_gid);
printf("size: %ld\n", info.st_size);
printf("modtime: %ld\n", info.st_mtime);
printf("name: %s\n", fname );
}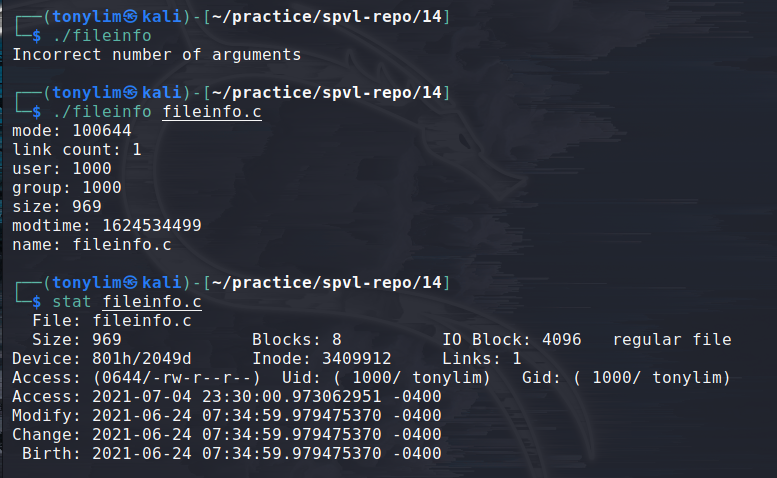
showing certain file's inode information.
'Operating System > System Programming(Arif Butt)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Lec16) Programming Terminal Devices (0) | 2021.07.08 |
|---|---|
| Lec15) Design and Code Of UNIX who Utility , Buffering (0) | 2021.07.06 |
| Lec13) UNIX File Management (0) | 2021.06.29 |
| Lec12) UNIX File System Architecture (0) | 2021.06.27 |
| Lec11) Design and Code of UNIX more utility (0) | 2021.06.25 |