기본 개념

RestTempate가 실제로 실행할 로직이 들어있는 RepeatCallback 각 스레드마다 실행시키게 된다.
RepeatCallback안에서 일어나는 Chunk process도 각 스레드마다 일어나게 된다.
스프링 배치 스레드 모델
- 기본적으로는 단일 스레드 방식으로 작업
- 성능 향상과 대규모 데이터 작업을 위한 비동기 처리 및 Scale out 기능을 제공한다.
- Local 과 Remote 처리를 지원한다.
AsyncItem Processor / Writer = 별도의 스레드가 할당되어 작업을 처리하는 방식
Multi-threaded step = Step 내 Chunk 구조인 ItemReader, Processor, Writer 마다 여러 스레드가 할당되어 실행하는 방법
Remote Chunking = 분산환경 처럼 Step 처리가 여러 프로세스로 분할되어 외부의 다른 서버로 전송되어 처리하는 방식
Parallel Steps = Step 마다 스레드가 할당되어 여러개의 Step을 병렬로 실행하는 방법
Partitinoing = Master / Slave 방식으로서 Master 가 데이터를 파티셔닝 한 다음 각 파티션에게 스레드를 할당하여 Slave 가 독립적으로 작동하는 방식
AsyncItemProcessor / AsyncItemWriter
기본개념
Step안의 ItemProcessor가 비동기적으로 동작하는 구조
AsyncItemProcessor 로부터 AsyncItemWriter 가 받는 최종 결과값은 List<Future<T>> 타입이며 비동기 실행이 완료될 떄까지 대기한다.
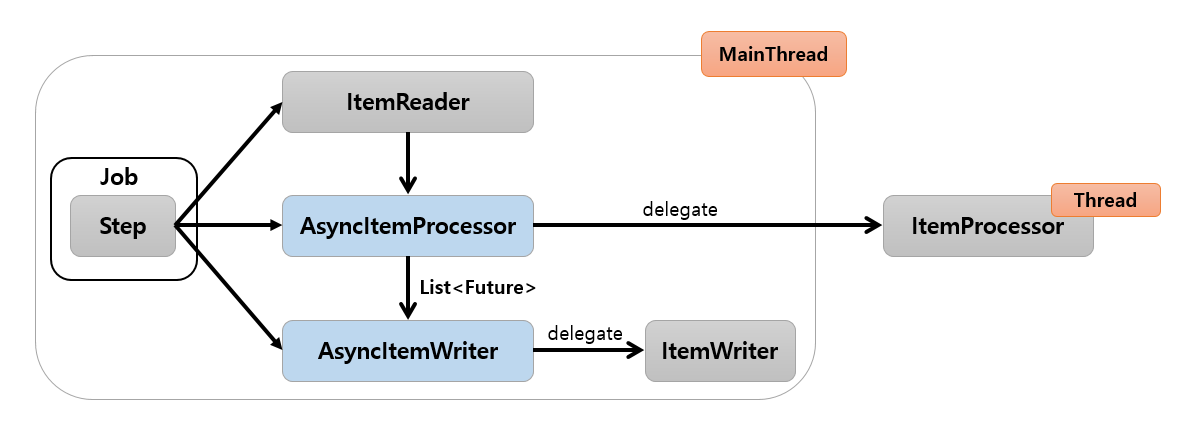

Future#get은 블록킹 메소드이기 때문에 ItemProcessor의 모든 비동기 작업이 끝나야 write를 할수 있게 된다.
@Bean
public AsyncItemProcessor asyncItemProcessor() throws Exception {
AsyncItemProcessor<Customer, Customer> asyncItemProcessor = new AsyncItemProcessor();
asyncItemProcessor.setDelegate(customItemProcessor());
asyncItemProcessor.setTaskExecutor(new SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor());
// asyncItemProcessor.setTaskExecutor(taskExecutor());
asyncItemProcessor.afterPropertiesSet();
return asyncItemProcessor;
}@Bean
public AsyncItemWriter asyncItemWriter() throws Exception {
AsyncItemWriter<Customer> asyncItemWriter = new AsyncItemWriter<>();
asyncItemWriter.setDelegate(customItemWriter());
asyncItemWriter.afterPropertiesSet();
return asyncItemWriter;
}일반적인 ItemProcessor 와 ItemWriter를 Bean으로 등록한 뒤에 setDelegate를 통해 전달하면 해당 로직들이 비동기적으로 동작하게 된다.
Multi-threaded Step
기본개념
- Step 내에서 멀티 스레드로 Chunk 기반 처리가 이루어지는 구조
- TaskExecutorRepeatTemplate 이 반복자로 사용되며 설정한 개수 (throttleLimit) 만큼의 스레드를 생성하여 수행함

각각의 스레드가 ItemReader -> Processor -> Write를 순차적으로 독립적으로 수행하게 된다.
ItemReader가 같은것을 읽어오거나 읽을 때 충돌이 나지 않기 위해 thread safe한 Reader를 구현하거나 사용해야한다.
JDBCPagingItemReader , JPAPagingItemReader가 thread safe한 상태로 제공이 된다.
thread safe한 ItemReader를 사용하지 않으면 중복된것을 읽어오거나 동시성 오류가 나게 된다.
Parallel Steps
기본개념
- SplitState 를 사용해서 여러 개의 Flow들을 병렬적으로 실행하는 구조
- 실행이 다 완료된 후 FlowExecutionStatus 결과들을 취합해서 다음 단계 결정을 한다.

SplitState에서 여러개의 Flow들을 들고 있고 TaskExecutor에서 각 스레드에서 각 Flow들을 실행 시키게 된다.
@Bean
public Job job() {
return jobBuilderFactory.get("batchJob")
.incrementer(new RunIdIncrementer())
.start(flow1())
.split(taskExecutor()).add(flow2(),flow3())
.next(flow4())
.end()
.listener(new StopWatchJobListener())
.build();
}split에서 병렬적으로 실행될 flow2 ,flow3들을 추가하고 이것들이 다 끝나고 나면
main thread에서 next에 있는 flow4를 실행시키게 된다.
Partitioning
기본개념
- MasterStep 이 SlaveStep 을 실행시키는 구조
- SlaveStep은 각 스레드에 의해 독립적으로 실행이 됨 , 독립적인 StepExecution 파라미터 환경을 구성함
- SlaveStep은 ItemReader/ ItemProcessor / ItemWriter 등을 가지고 동작하며 작업을 독립적으로 병렬 처리한다.
- MasterStep은 PartitionStep이며 SlaveStep은 TaskletStep , FlowStep등이 올 수 있다.
MasterStep은 논리적인의미이지 실제로는 그냥 Step이다.
PartitionStep (MasterStep 역할을 함)
- 파티셔닝 기능을 수행하는 Step 구현체
- 파티셔닝을 수행후 StepExecutionAggregator를 사용해서 StepExecution의 정보를 최종 집계한다.
PartitionHandler
- ParitionStep에 의해 호출되며 스레드를 생성해서 WorkStep 을 병렬로 실행한다.
- WorkStep에서 사용할 StepExecution생성은 StepExecutionSplitter 와 Partitioner 에게 위임한다.
- WorkStep을 병렬로 실행 후 최종결과를 담은 StepExecution을 PartitionStep에 반환한다.
StepExecutionSplitter
- WorkStep에서 사용할 StepExecution을 gridSize만큼 생성한다.
- Partitioner를 통해 ExecutionContext를 얻어서 StepExecution에 매핑한다.
Partitioner
- StepExecution에 매핑할 ExecutionContext를 gridSize만큼 생성한다.
- 각 ExecutionContext에 저장된 정보는 WorkStep을 실행하는 스레드마다 독립적으로 참조 및 활용이 가능하다.
결국 Step을 실행시키기위해서 필요한 StepExecution , ExecutionContext를 만드는 과정이다.

각 스레드마다 StepExecution , ExecutionContext를 지니고 있다.

@JobScope 한것처럼 Proxy객체가 생성되고 런타임에 실제 요청을 처리할시에 하위의 ItemReader,processor, writer 빈들이 생성이 된다.
이들은 각 스레드마다 생성이 되기에 공유가 되지않아서 thread safe하다.
SynchronizedItemStreamReader
기본개념
- Thread-safe 하지 않은 ItemReader 를 Thread-safe하게 처리하도록 하는 역할
- Spring Batch 4.0 부터 지원한다.

synchronized로 동기화 처리하여 기다리게 해서 동시성 이슈를 해결한다.
실제 데이터처리는 JdbcCursorItemReader에게 위임한다.
@Bean
@StepScope
public SynchronizedItemStreamReader<Customer> customItemReader() {
JdbcCursorItemReader<Customer> notSafetyReader = new JdbcCursorItemReaderBuilder<Customer>()
.fetchSize(60)
.dataSource(dataSource)
.rowMapper(new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Customer.class))
.sql("select id, firstName, lastName, birthdate from customer")
.name("SafetyReader")
.build();
return new SynchronizedItemStreamReaderBuilder<Customer>()
.delegate(notSafetyReader)
.build();
}랩핑해줘서 동기화를 시키고 실제 item 을 읽어오는 itemReader는 JdbcCursorItemReader를 통해서 읽어오는 것이다.
'WEB > Spring Batch' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 실전! 스프링 배치 어플리케이션 개발 (0) | 2023.04.11 |
|---|---|
| 스프링 배치 이벤트 리스너 & 스프링 배치 테스트 및 운영 (0) | 2023.04.04 |
| 스프링 배치 반복 및 오류 제어 (1) | 2023.03.25 |
| 스프링 배치 청크 프로세스 활용 - ItemWriter , ItemProcessor (0) | 2023.03.24 |
| 스프링 배치 청크 프로세스 활용 - ItemReader (0) | 2023.03.23 |