$ wc 0< /etc/passwd == redirecting filedescriptor 0 as /etc/passwd
$ wc /etc/passwd == taking as cmd line argument
$ cat < file1 >file2 == $ cat >f2 <f1 == $ <f1 >f2 cat
per process file descriptor table (ppfdt) = file descriptor 0 as file1 , file descriptor 1 as file2
$ cp file1 file2
$ cat <file1 >file2 == takes file1's content as input and spit it out to file2
$ cat 0<f1 1>op 2>err == if f1 doesn't exist the error message will pop out in terminal since ppfdt is still same as base case

$ cat f1 1>op 2>err == f1 is passed as command line argument since file descriptor 1,2 is alreay redirected error message will go to err file

for more explain == Bash One-Liners Explained, Part III: All about redirections (catonmat.net)
Bash One-Liners Explained, Part III: All about redirections
This is the third part of the Bash One-Liners Explained article series. In this part I'll teach you all about input/output redirection. I'll use only the best bash practices, various bash idioms and tricks. I want to illustrate how to get various tasks don
catonmat.net
Inter Process Communication(IPC)
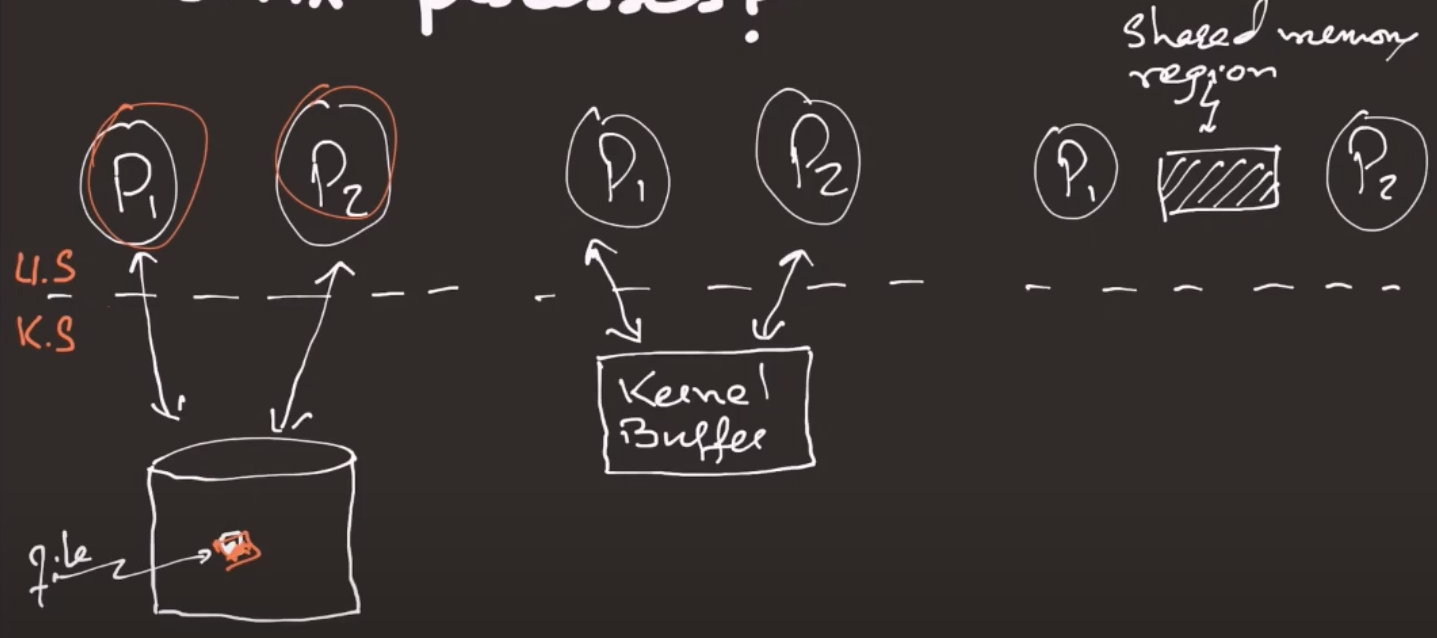
1. was very slow because it includes Disk IO
2. used Kernel Buffer, switching from user mode to kernel mode and vice versa take time
3. use shared memory , using systemV shared memory api

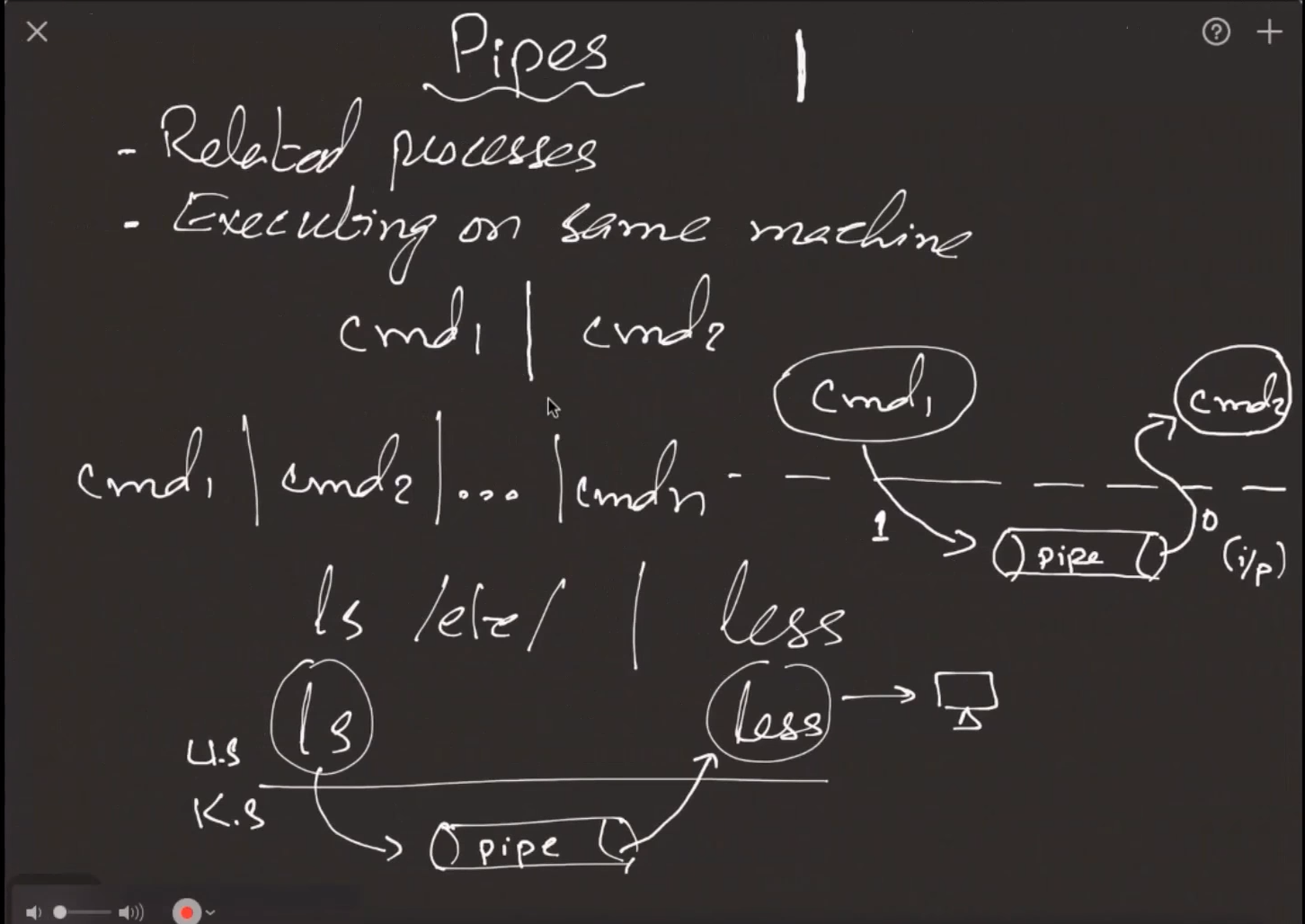
pipe is manage by kernel
tee cmd

tee command takes standard input and wirte it on the disk(files) and stdout
Named Pipe
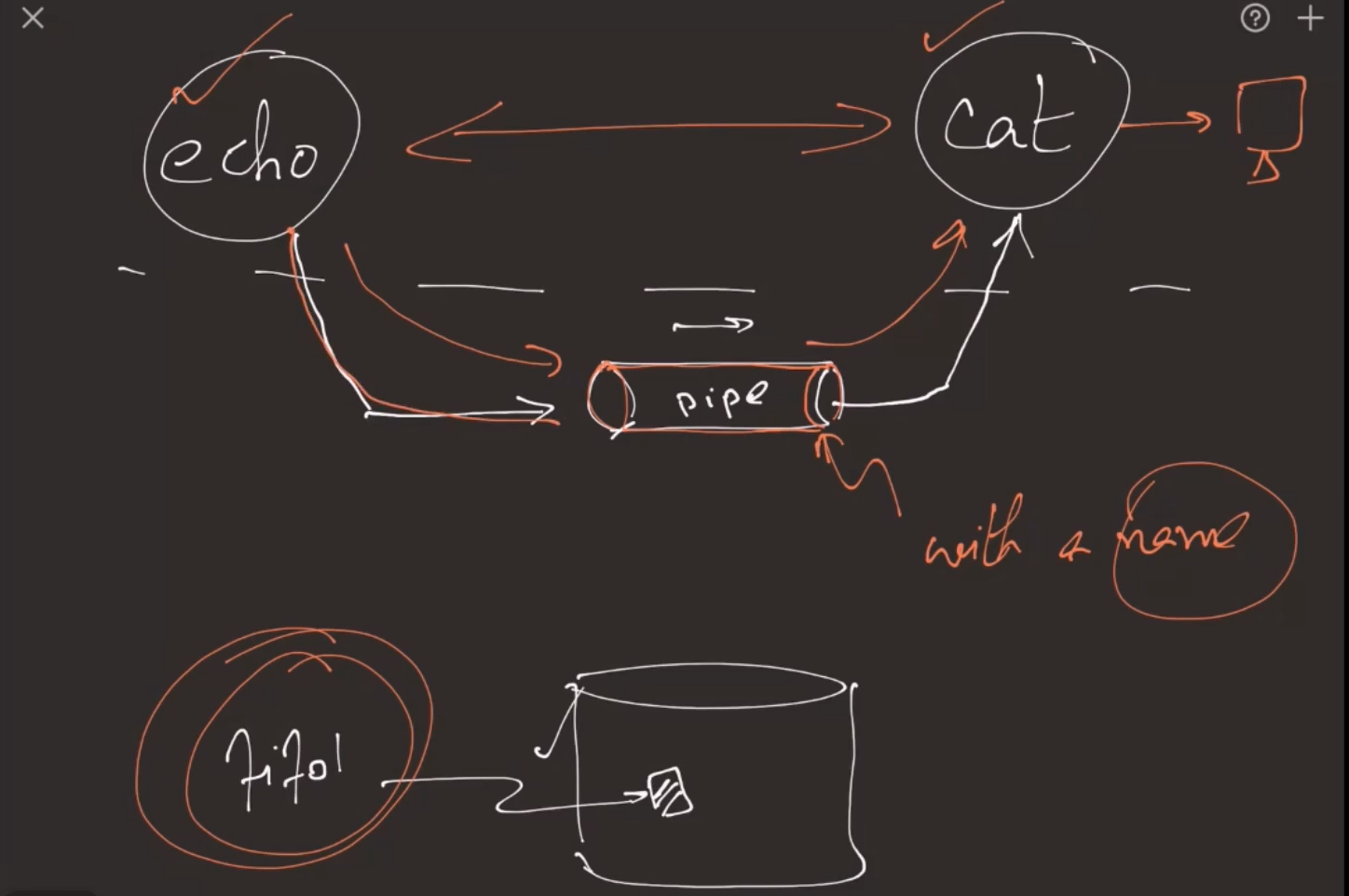
no data actually goes to fifo1 file , instead kernel creates pipe and redirect those input and oupt.
echo "something" > fifo1 == process is blocked
in the other terminal when we $ cat fifo1 we can see "something" on screen and blocked process gets terminated
'Operating System > O.S(Arif Butt)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| /proc directory , software Installation (Lec12,Lec13) (0) | 2021.01.16 |
|---|---|
| Task scheduling (Lec13) (0) | 2021.01.14 |
| Signal, Process scheduling (Lec10, Lec11) (0) | 2021.01.09 |
| Basic Shell Command (Lec06, Lec07) (0) | 2021.01.01 |
| Linux Environment (Lec01, Lec02) (0) | 2020.12.29 |